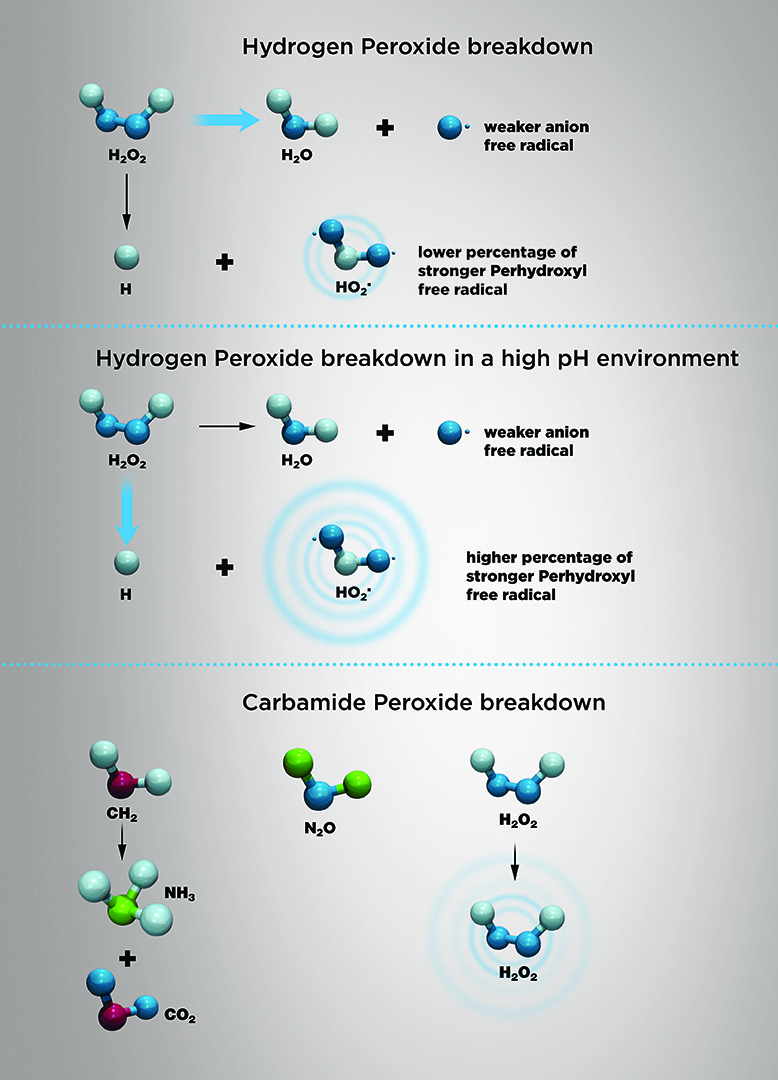
· Carbamide peroxide is a third as strong as Hydrogen Peroxide, so a 30% solution is equivalent to a 10% solution of Hydrogen peroxide Hydrogen Peroxide is typically he active ingredient in office bleaching systems These are applied to create more active, rapid bleaching effect after the application of a liquid dam to protect the gum tissue · Potočnik et al (00) evaluated the effect of 10% carbamide peroxide on the human enamel subsurface layer in terms of microhardness, microstructure, and mineral content They found that 10% carbamide peroxide caused clinically insignificant local microstructural and chemical changes in enamel · Carbamide peroxide (CP) is widely used as a toothwhitening agent in selfadministered toothbleaching products In this study, the effects of 5% and 10% CP on dentinal collagen structure and chemical properties were evaluated in vitro
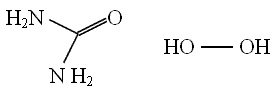
Glossary Carbamide Peroxide
What is difference between carbamide peroxide and hydrogen peroxide
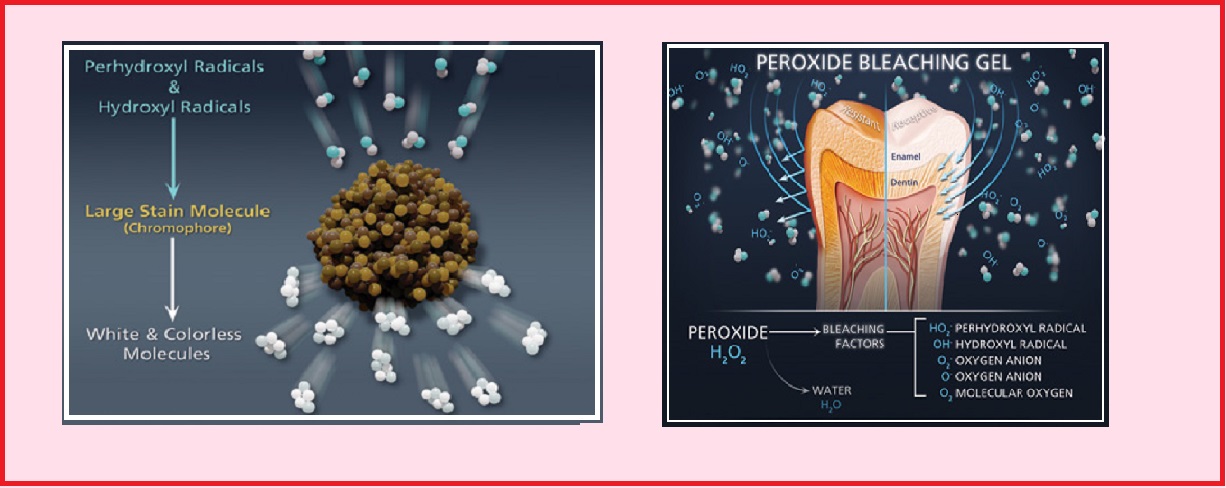
What is difference between carbamide peroxide and hydrogen peroxide-Carbamide Peroxide – How It's Used Carbamide peroxide is basically a compound that consists of hydrogen peroxide and urea It has a bleaching effect on our teeth and that is why this compound is now being regularly used for the making of the latest teeth whitening products available on the market today · Carbamide peroxide, upon coming in contact with water, ends up releasing hydrogen peroxide Bleaching is essentially an oxidation reaction where the bleach (hydrogen peroxide) oxidizes the double bond in tooth stains (chromogen), causing the chromogen to change its chemical structure



Carbamide An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
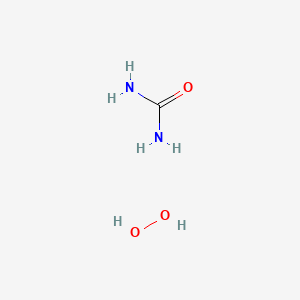
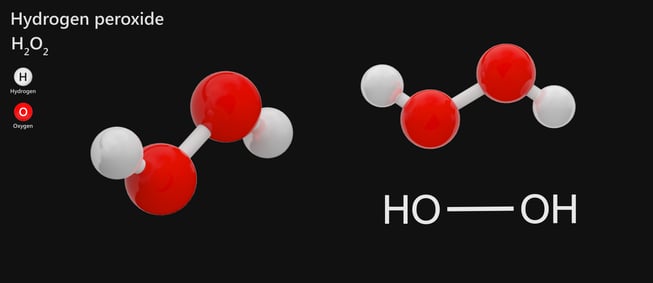
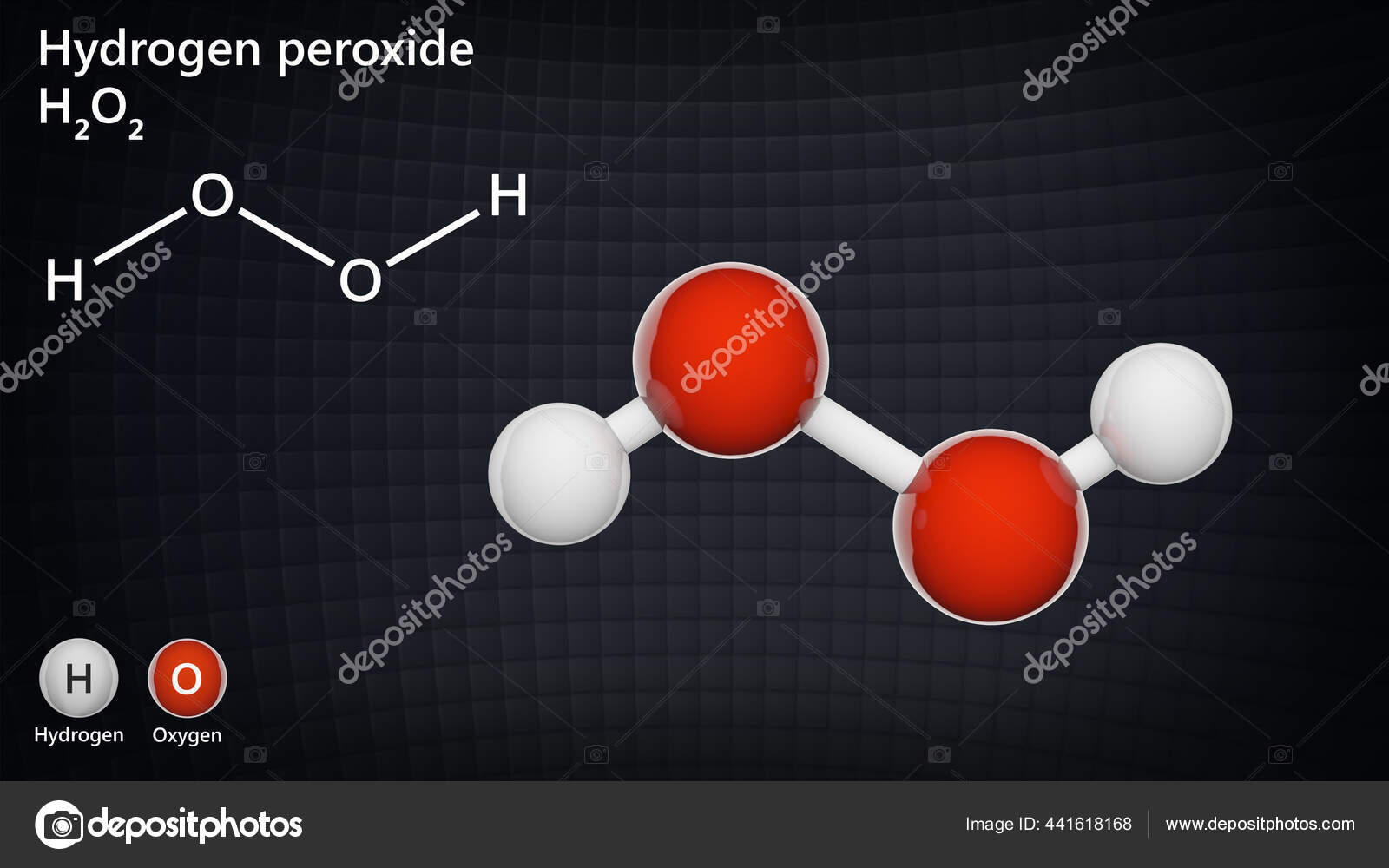
Hydrogen peroxide is a chemical compound with the formula H 2 O 2In its pure form, it is a very pale blue liquid, slightly more viscous than waterIt is used as an oxidizer, bleaching agent, and antisepticConcentrated hydrogen peroxide, or "hightest peroxide", is a reactive oxygen species and has been used as a propellant in rocketryIts chemistry is dominated by the O–O bondAnatomical Therapeutic Chemical (ATC) classification BRbr003 B BLOOD AND BLOOD FORMING ORGANS B05 BLOOD SUBSTITUTES AND PERFUSION SOLUTIONS B05B IV SOLUTIONS B05BC Solutions producing osmotic diuresis B05BC02 Carbamide D033 Carbamide peroxide (USP) D DERMATOLOGICALS D02 EMOLLIENTS AND PROTECTIVES D02ASynonym Carbamide Per hydrate, Carbamide peroxide, Hydrogen peroxide–Urea adduct, Percarbamide, Urea hydrogen peroxide Linear Formula CO(NH 2 )
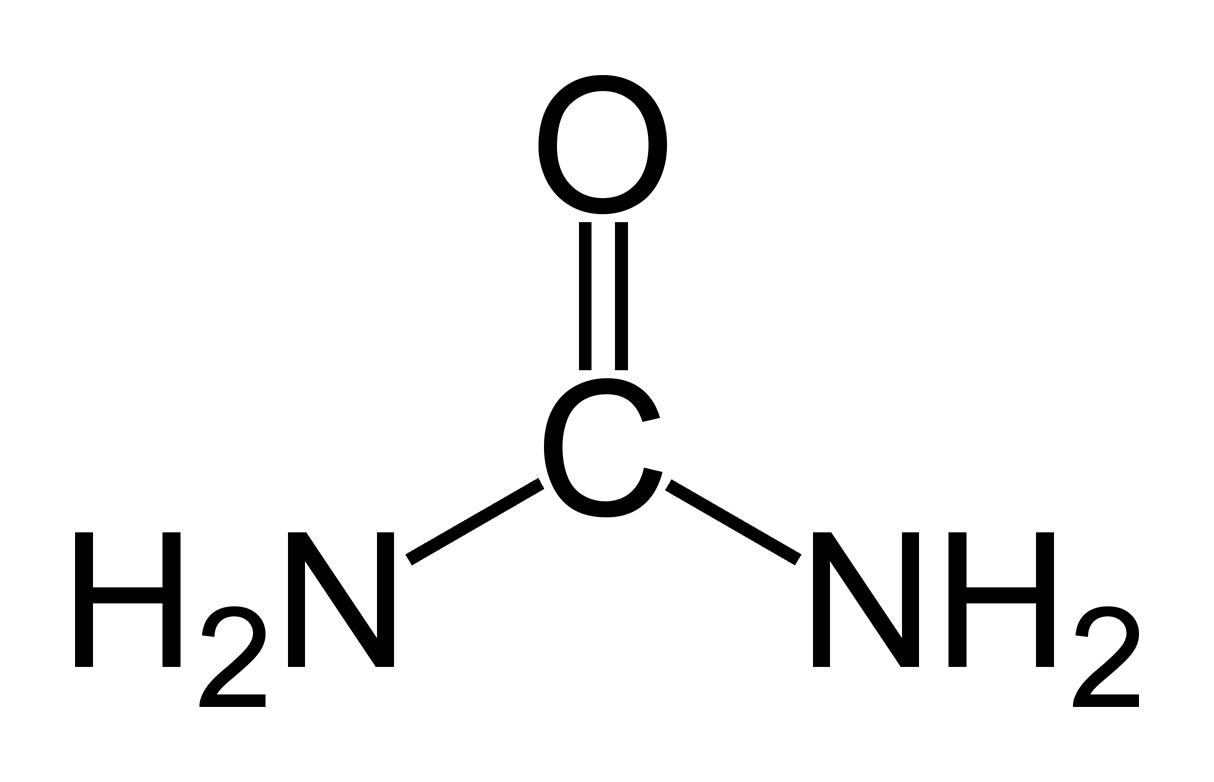
· Carbamide peroxide bleaching agents have raised important questions on their potential adverse effects on the structure of enamel The purpose of this study was to examine the effects of three carbamide peroxide bleaching agents in different concentrations (10, 16 and 35%) on the structure of enamelHydrogen peroxide–Urea adduct Carbamide peroxide, also called urea peroxide, urea hydrogen peroxide, and percarbamide, is an oxidising agent, consisting of hydrogen peroxide compounded with urea The molecular formula is CH6N2O3, or CH4N2OH2O2 It is a white crystalline solid that releases oxygen in contact with water The chemical is a skinCarbamidePeroxide chemical information, properties, structures, articles, patents and more chemical data
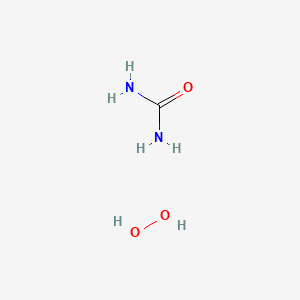
Carbamide peroxide is an adduct of urea and hydrogen peroxide which on contact with water break down to urea and hydrogen peroxideBackground Tooth bleaching (whitening) is a conservative and cost effective treatment of discoloured teeth Objectives The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinical efficacy and safety of 16% and 35% carbamide peroxide as inoffice bleaching agents Methods Thirty adult subjects who desired to whiten their discoloured teeth were enrolled in the studyCarbamide peroxide, (CH 4 N 2 OH 2 O 2), is a chemical that contains hydrogen peroxide and urea – an organic compound Its structural formula is Its structural formula is Pure carbamide peroxide has the form of white crystals or crystal powder, is soluble in water, and contains approximately 35% hydrogen peroxide


Hydrogen Peroxide Urea Ch6n2o3 Chemspider



A Review On Dental Whitening Sciencedirect
Bleaching is a chemical method that involves the chemical degradation through oxidation, of chromagens Both carbamide peroxide and hydrogen peroxide act in the same way In fact, to put it more avidly, carbamide peroxide is a stable form of hydrogen peroxide that breaks down when you add it to water and in turn releases hydrogen peroxideUreas describes a class of chemical compounds that share the same functional group, a carbonyl group attached to two organic amine residues RR'N—CO—NRR' Examples include carbamide peroxide, allantoin, and hydantoin Ureas are closely related to biurets and related in structure to amides, carbamates, carbodiimides, and thiocarbamidesCarbamide Peroxide, chemical structure, molecular formula, Reference Standards Carbamide Peroxide CH 6 N 2 O 3 9407 Urea,compdwith hydrogen peroxide (11) Urea compound with hydrogen peroxide (11) »Carbamide Peroxide contains not less than 960percent and not more than 10percent of CH 6 N 2 O 3


Dental Enamel Bleached For A Prolonged And Excessive Time Morphological Changes


Carbamide Peroxide
· The study was conducted on 125 human third molars dissected into quarters for separate enamel and dentin measurements The bleaching process was performed with 38% and 25% hydrogen peroxide (HP) and 30%, 16%, and 10% carbamide peroxide (CP) gels two times for 15 minutes each timeThe purpose of this study was to examine the effects of three carbamide peroxide bleaching agents in different concentrations (10, 16 and 35%) on the structure of enamel Forty enamel slabs prepared from human third molars were divided equally among four groups The specimens in the first and second group were subjected to 10% or 16% carbamide · Carbamide Peroxide and Hydrogen Peroxide An ingredient often used in dental whitening gels is carbamide peroxide, a common bleaching agent in many dental products It's a source of hydrogen peroxide, which bleaches teeth through a reaction with existing stains, changing their chemical structure to remove discoloration



Carbamide Peroxide 124 43 6 Buy Active Oxygensolid Disinfector Manufacturer Carbamide Peroxide 124 43 6 Carbamide Peroxide 124 43 6 Carbamide Peroxide 124 43 6 Product On Alibaba Com



Carbamide Peroxide Nanoparticles For Dental Whitening Application Characterization Stability And In Vivo In Situ Evaluation Sciencedirect
Urea Peroxide, also known as carbamide peroxide, is made up of both urea and hydrogen peroxide in equal parts It is used as a source of hydrogen peroxide for disinfection, bleaching and oxidation sometimes in dental applications Ungrad · • Carbamide peroxide has hydrogen peroxide in it connected with urea • When dissolving, carbamide peroxide releases hydrogen peroxide • Hydrogen peroxide is a faster and strong oxidizer than carbamide peroxide Since • the releasing of hydrogen peroxide from carbamide peroxide is slower and limited, it is a better teeth whiteningCarbamide peroxide, also called urea peroxide, is an oxidising agent, consisting of hydrogen peroxide compounded with urea The molecular formula is CH6N2O3, or CH4N2OH2O2 It is white crystalline material that releases oxygen in contact with water



Hydrogen Peroxide Urea Wikipedia



Amazon Com Teeth Whitening Kit Usa Dentists Recommended Crystal Clear Teeth Whitening Kit Professional Led Light 35 Carbamide Peroxide 6x 5ml Gel Syringes And Tray Health Personal Care
Carbamide peroxide (USP) chemical information, properties, structures, articles, patents and more chemical dataCarbamide peroxide can be stabilized by both chemical additives and/or thermal as an anhydrous base and "acidifiers," 43 allowing the whitening gels to be fully aqueous base and at or above pH 7 49 Carbamide peroxide requires a controlled decomposition into hydrogen peroxide and as well as the Xray structure of pentagonalSearch chemicals by name, molecular formula, structure, and other identifiers Find chemical and physical properties, biological activities, safety and toxicity information, patents, literature citations and more We are constantly adding new data and working on improving interfaces to chemical information Please check back often!


Effect Of Carbamide Peroxide Based Bleaching Agents Containing Fluoride Or Calcium On Tensile Strength Of Human Enamel



Tooth Whitening Pocket Dentistry
M Strauss, Chem Zentralbl 11, 0 (1913) Use for prepn of H 2 O 2 J Milbauer, Chem Ztg 35, 871 (1911 · Background Tooth whitening is one of the most requested dental treatments, but it still presents some side effects Indeed, the bleaching agent can generate patients' discomfort and dental hard tissue damages, not achieving an efficient and longlasting treatment with optimum whitening effect To overcome these limitations, the bleaching agents containing nanoCarbamide Peroxide is used as both an antiseptic and disinfectant when mixed with water Ungraded products supplied by Spectrum are indicative of a grade suitable for general industrial use or research purposes and typically are not suitable for human consumption or therapeutic use



Calameo Kor Night 16 Carbamide Peroxide Sds


Effects Of Different Concentrations Of Carbamide Peroxide And Bleaching Periods On The Roughness Of Dental Ceramics
Answer Our product contains 22% of the carbamide peroxide We understand most of our competitors use 35% of carbamide peroxide, but studies show that 18% carbamide peroxide already working well Plus, we are trying our best to make the teeth whitening process to be nonsensitivity and painfree, it is better in the long runHydrogen peroxide and carbamide peroxide bleachin agents at different concentrations were included on analysis The United States Pharmacopeia and International Standard methods was used to determine the amount of peroxide, in the agents of different brands and concentrations after products storage at 3°C, °C and 40°C by 8 days · Then why is carbamide peroxide used?


The Difference Between Whitening Products With Hydrogen Peroxide And Carbamide Peroxide Dental Supplies And Equipment Dentaltix



Hydrogen Peroxide Chemical Equation Formula
Hydrogen peroxide carbamimidic acid (11) SMILES C(=N)(N)OOO Copy Std InChi InChI=1S/CH4N2OH2O2 /c21(3)4;12/h(H4,2,3,4);12H Copy Std InChIKey AQLJVWUFPCUVLOUHFFFAOYSAN Copy Cite this record CSID, http//wwwchemspidercom/ChemicalStructureLiterature References Prepn GB 1555 (1911 to Bayer); · Hydrogen peroxide changes the chemical structure of the tooth surface and removes the stains and the discoloration from the tooth leaving them white and bright in color Types of teeth whitening gel There are typically two types of teeth whitening gels that are categorized based on their rate of action on the tooth surface
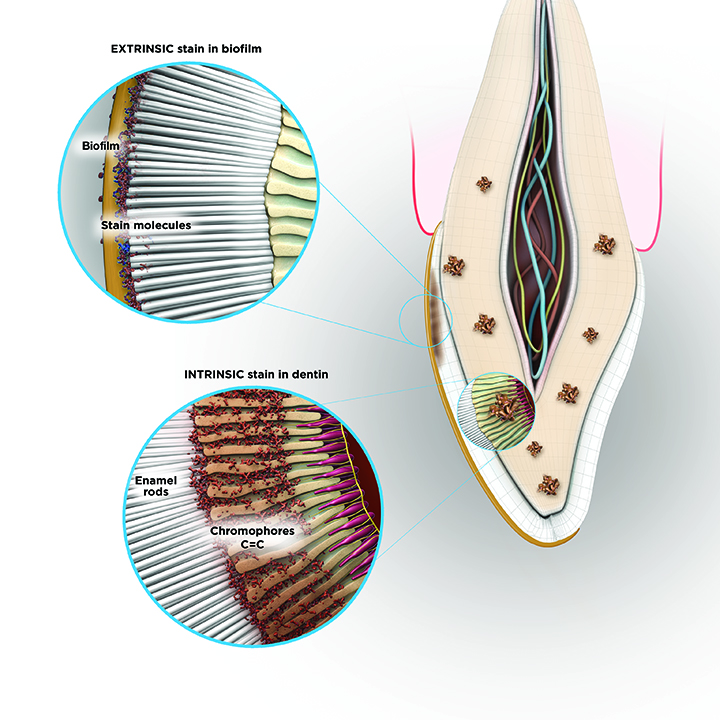


Teeth Whitening Technology Volume 13 Issue 3 Inside Dentistry
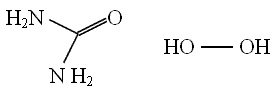


Glossary Carbamide Peroxide
· Carbamide peroxide, for example, is a slowacting bleach that when applied to teeth will react, breaking down into hydrogen peroxide and urea Urea is a waste product, but the hydrogen peroxide removes superficial stains and deeper discoloration by altering their chemical structureCarbamide peroxide can be used in whitener formulations because when it's exposed to water it breaks down into hydrogen peroxide (and urea), which then breaks down and creates the whitening effect as described above Carbamide peroxide is used because it's a comparatively stable compound This helps theCarbamide peroxide otic (for the ears) is used to soften and loosen ear wax, making it easier to remove Carbamide peroxide may also be used for purposes not listed in this medication guide



Effectiveness Of Home Bleaching Agents In Discolored Teeth And Influence On Enamel Microhardness Abstract Europe Pmc


Effect Of Carbamide Peroxide Based Bleaching Agents Containing Fluoride Or Calcium On Tensile Strength Of Human Enamel
Carbamide Peroxide is approximately 1/3 the strength of Hydrogen Peroixde and is not recommended for chairside application Carbamide Peroxide has a lengthy chemical bond similar to a shell covering a nut The shell must break down to release the hydrogen peroxide and this takes time away from the chairside treatment · What is carbamide peroxide?Bleaching is defined here as the chemical degradation of the chromogens The active ingredient in most whitening products is hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) which is delivered as hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide Carbamide peroxide is a stable complex that breaks down in contact with water to release hydrogen peroxide



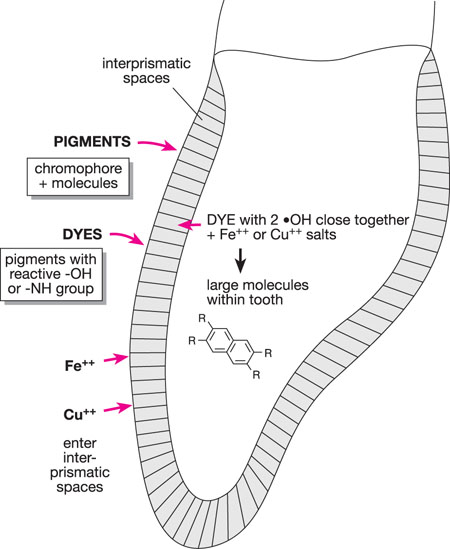
Oral Care Products Outline Tooth Anatomy Dental Caries


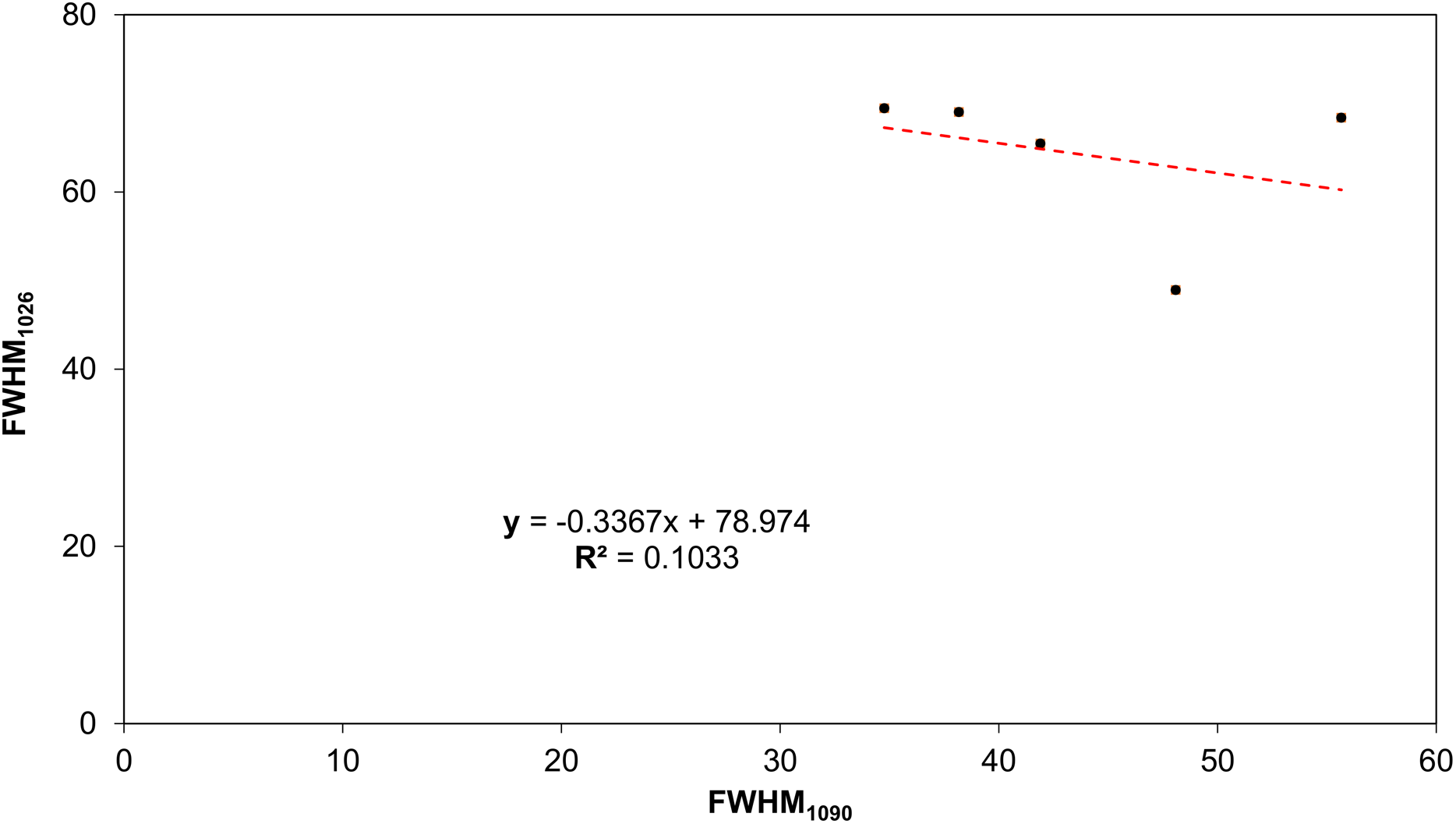
Spectroscopic Criteria For Early Diagnosis Of Changes In The Mineral And Organic Matrix Of Hard Dental Tissues
Synonym Carbamide Per hydrate, Carbamide peroxide, Hydrogen peroxide–Urea adduct, Percarbamide, Urea hydrogen peroxide Linear Formula CO(NH 2 )Charkit Chemical Company is supplier for Carbamide peroxide Charkit services the Fine Chemical Industry, particularly the Pharmaceutical, Personal Care, Flavor & Fragrance and Imaging sectors With our many supplier relationships and contacts, Charkit bridges the gap between customer need and reliable supply with unparalleled service and theCarbamide peroxide, (CH 4 N 2 O·H 2 O 2), is a chemical that contains hydrogen peroxide and urea – an organic compound Pure carbamide peroxide has the form of white crystals or crystal powder, is soluble in water, and contains approximately 35% hydrogen peroxide
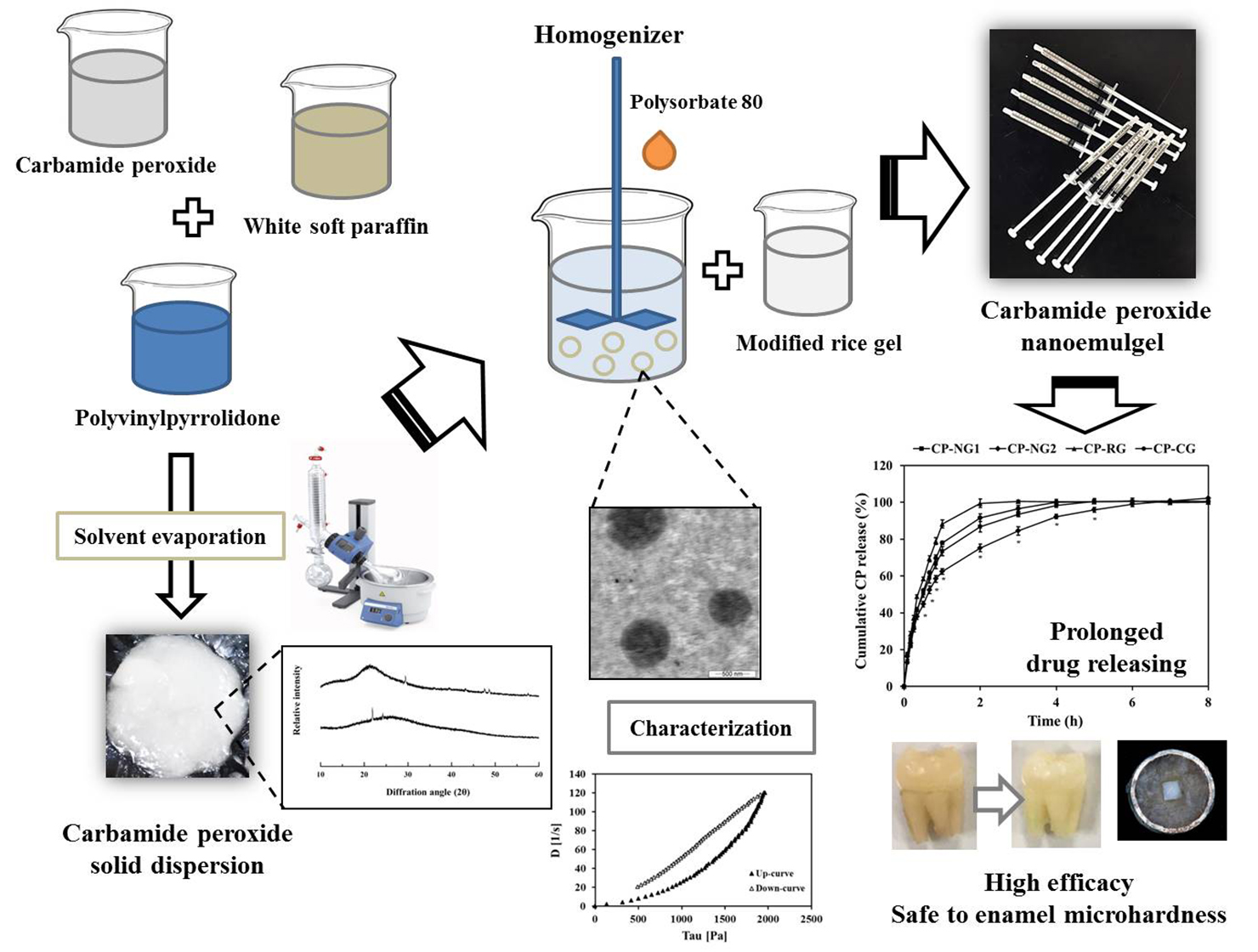


Pharmaceuticals Free Full Text Development Of Controlled Release Carbamide Peroxide Loaded Nanoemulgel For Tooth Bleaching In Vitro And Ex Vivo Studies Html



Pdf Radicular Peroxide Penetration From Carbamide Peroxide Gels During Intracoronal Bleaching Osman Saka Academia Edu
· Carbamide Peroxide USP & Pure Grade Manufacturers, with SDS GHS MSDS Sheet Muby Chemicals of Mubychem Group, established in 1976, is the original manufacturers of Specialty Chemicals, Pharmaceutical Excipient, Fragrance Food & Flavor chemicals, Reagent Grade Chemicals, Shale Gas Fracturing Chemicals in India Mubychem Group has severalChemical formula CH6N2O3 Drugbank ID DB Chemical structure of carbamide peroxide Click to enlargePočet řádků 8 · Carbamide peroxide, also known as ureahydrogen peroxide, is a watersoluble, white crystalline



Urea Peroxide New Substitute Chemical For Urea Co Nh 2 H 2 O 2 Also Named Carbamide Peroxide



Carbamide An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
· Carbamide peroxide, an ingredient used in toothpaste, is a peroxygen that combats oral biofilms that cause tooth discoloration and halitosis (bad breath) 15 Last, ozone gas is a peroxygen with disinfectant qualities and is used to clean air or water supplies Overall, peroxygens are highly effective and commonly used, with no associated



Woa1 Tooth Whitening Composition Google Patents



Carbamide Peroxide 99 Dental Stable B C Dye Chem Indore Id


Teeth Whitening Technology Volume 13 Issue 3 Inside Dentistry



Effects Of 45s5 Bioglass On Surface Properties Of Dental Enamel Subjected To 35 Hydrogen Peroxide Topic Of Research Paper In Medical Engineering Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On



Scielo Brasil Effect Of Violet Led Light On In Office Bleaching Protocols A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial Effect Of Violet Led Light On In Office Bleaching Protocols A Randomized Controlled Clinical Trial



Localized In Vitro Exposure Of Carbamide Peroxide Gel To Extracted Download Scientific Diagram



Buy Mysmile Teeth Whitening Kit With Led Light 3 Non Sensitive Teeth Whitening Gel And Tray Deluxe 10 Min Fast Result Carbamide Peroxide Teeth Whitener Help Remove Teeth Stain From Coffee Drinks Food Online



Concentrations Use And Brands Of Hydrogen And Carbamide Peroxides Download Table



Urea Hydrogen Peroxide 1 G Tablets Stabilized Contains 35 Wt H2o2 Acros Organics 5kg Plastic Bucket Urea Hydrogen Peroxide 1 G Tablets Stabilized Contains 35 Wt H2o2 Acros Organics Fisher Scientific


Shear Bond Strength After Dentin Bleaching With 10 Carbamide Peroxide Agents


Benzoyl Peroxide Wikipedia



Phenylpiracetam Racetams Nootro Phenylpiracetam Racetams Carbamide Peroxide Chemical Structure Hd Png Download 1024x1217 Pngfind



Landolt Bornstein Online Search



Vital Tooth Bleaching
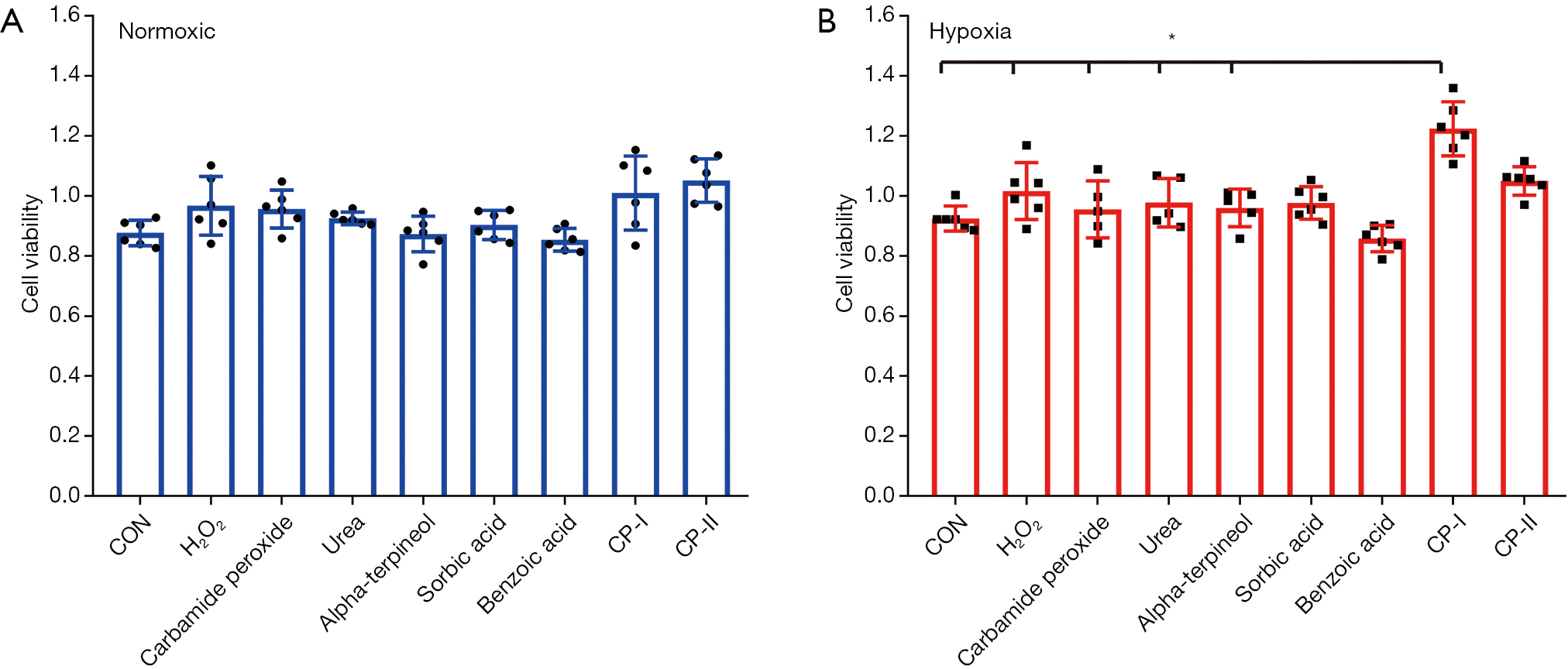


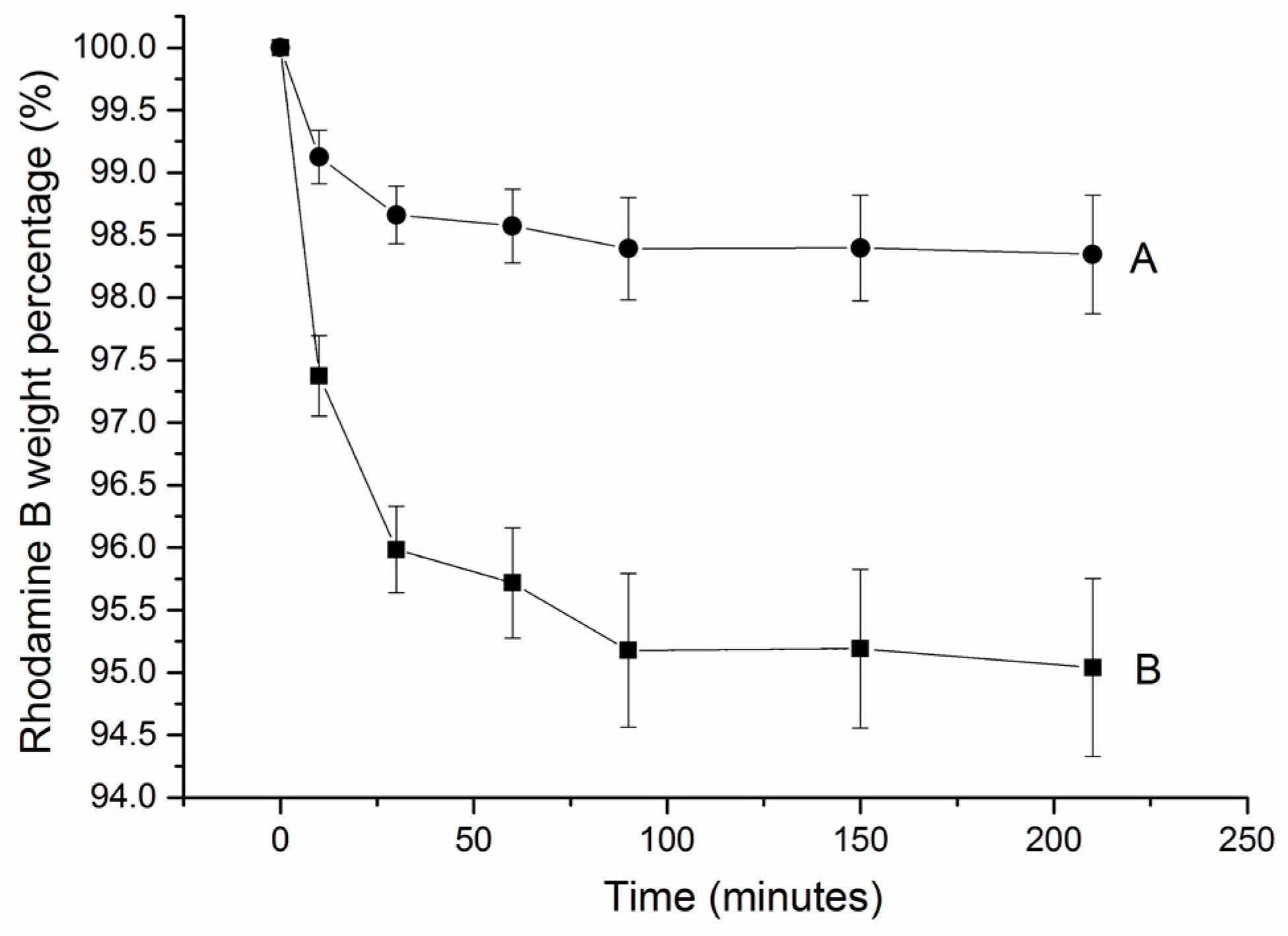
Slow Release Of Oxygen From Carbamide Peroxide For Promoting The Proliferation Of Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells Under Hypoxia Meng Annals Of Translational Medicine



Woa1 Antifungal Topical Composition For The Use In The Treatment Of Onychomycosis Google Patents



Preparation Optimization And Release Behaviour Evaluation Of Carbamide Peroxide Microcapsules Integrated With Eudragit Rs Xu Chemistryselect Wiley Online Library


Evonik Purchases Hydrogen Peroxide Producer In The Resonance Structure Of Anthracene Hd Png Download 00x873 Pngfind



Cas No 124 43 6 Sigma Aldrich


Best Way To Bleach Hair With Hydrogen Peroxide Best Way To Bleach Hair With Hydrogen Peroxide Visa
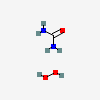


Carbamide Peroxide Ch6n2o3 Pubchem



Effect Of Tooth Bleaching On The Carbonate Concentration In Dental Enamel By Raman Spectroscopy Abstract Europe Pmc


Hydrogen Peroxide Caution 53 Usd


Bioline International Official Site Site Up Dated Regularly


Phenylpiracetam Racetams Nootro Phenylpiracetam Racetams Carbamide Peroxide Chemical Structure Hd Png Download 1024x1217 Pngfind



Role Of Fluoridated Carbamide Peroxide Whitening Gel In The Remineralization Of Demineralized Enamel An In Vitro Study Bollineni S Janga Rk Venugopal L Reddy Ir Babu P R Kumar Ss J



Carbamide Peroxide Spectrum Fisher Scientific


Hydrogen Peroxide Urea Wikipedia


Chemidplus 124 43 6 Aqljvwufpcuvlo Uhfffaoysa N Carbamide Peroxide Usp Similar Structures Search Synonyms Formulas Resource Links And Other Chemical Information



Peroxide An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Benzoyl Peroxide Wikipedia


Urea Hydrogen Peroxide Drug Information Uses Side Effects Chemistry Pharmacompass Com


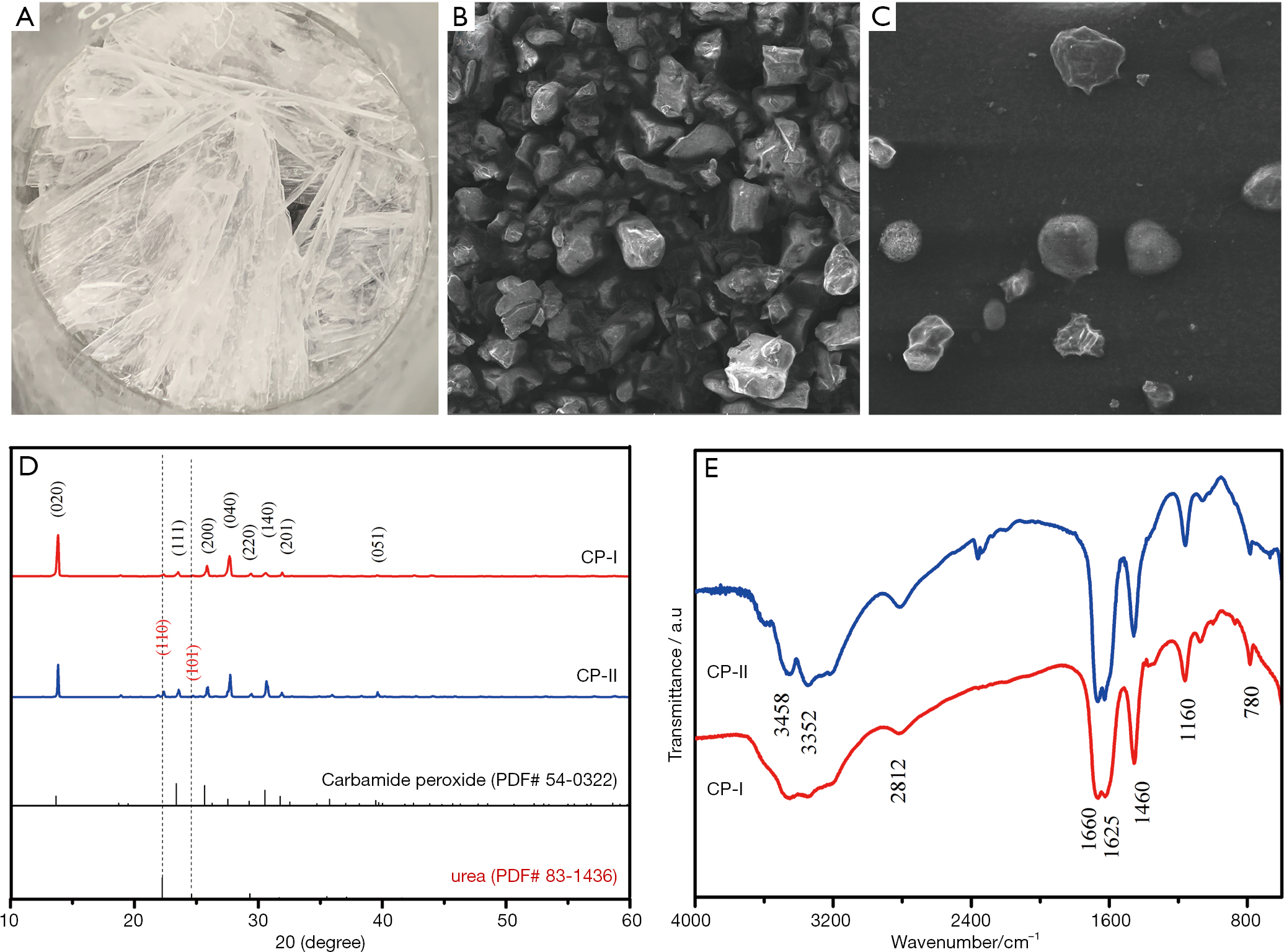
Dentistry Journal Free Full Text A Study For Tooth Bleaching Via Carbamide Peroxide Loaded Hollow Calcium Phosphate Spheres Html


Slow Release Of Oxygen From Carbamide Peroxide For Promoting The Proliferation Of Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells Under Hypoxia Meng Annals Of Translational Medicine



Pdf Stability Of Carbamide Peroxide In Gel Formulation As Prepared In Brazilian Compounding Pharmacies


Spectroscopic Criteria For Early Diagnosis Of Changes In The Mineral And Organic Matrix Of Hard Dental Tissues



The Effect Of Bleaching Agents On Micro Chemical Structure Of Human Enamel By Ftir Spectroscopy Method An In Vitro Study Semantic Scholar



Figure 2 From Stability Of Carbamide Peroxide In Gel Formulation As Prepared In Brazilian Compounding Pharmacies Semantic Scholar



Carbamide Peroxide



8



Carbamide Peroxide Rs 1750 00 Kg A B Enterprises Id


Carbamide Peroxide


Applications Of Lasers And Dental Bleaching In Dentistry Chemistry Behind Lasers And Dental Bleaching



Hydrogen Peroxide Urea Wikipedia



Pdf The Effects Of Seven Carbamide Peroxide Bleaching Agents On Enamel Microhardness Over Time Semantic Scholar


Bioline International Official Site Site Up Dated Regularly



Woa1 Bleaching Gel Google Patents



Bleaching Techniques Bleaching Agents Composition Manufacturer Ph Download Table



Pdf Stability Of Carbamide Peroxide In Gel Formulation As Prepared In Brazilian Compounding Pharmacies Semantic Scholar


Hydrogen Peroxide Storage Handling And Safety Requirements A Complete Guide


1 Chemistry And Safety Of Dental Bleaching Pocket Dentistry


1p Lsd Chemical Structure Hd Png Download 10x9 Pngfind


Carbamide Peroxide Ch6n2o3 Pubchem



Pdf Effect Of Different Concentrations Of Carbamide Peroxide And Green Tea Extract On The Color And Shear Bond Strength Of Enamel An In Vitro Study Ip Innovative Publication Pvt Ltd



Shutterstock Puzzlepix



Carbamide Peroxide Refill Large X 10ml Teeth Whitening



Teeth Whitening Kit With Led Light 10 Minute Fast Result Teeth Whitening Light Carbamide Peroxide Teeth Whitener With 3 Non Sensitive Teeth Whitening Gel To Removes Teeth Stain Mouth Tray Included Pricepulse


Carbamide Peroxide Chemical Structure Molecular Formula Reference Standards



Teeth Whitening Kit Teeth Whitening Light With 3 Non Sensitive Teeth Whitening Gel Carbamide Peroxide Teeth Whitening Pen For Home Travel Tooth Whitening 10 Min Fast Result Teeth Whitener Walmart Canada


Atr Ftir Eds And Sem Evaluations Of Enamel Structure After Treatment With Hydrogen Peroxide Bleaching Agents Loaded With Nano Hydroxyapatite Particles Peerj



Carbamide Peroxide American Chemical Society


Carbamide Peroxide Muby Chemicals



Carbamide Peroxide 124 43 6 Buy Active Oxygensolid Disinfector Manufacturer Carbamide Peroxide 124 43 6 Carbamide Peroxide 124 43 6 Carbamide Peroxide 124 43 6 Product On Alibaba Com


Structural Chemical Formula Molecular Structure Hydrogen Peroxide H2o2 Chemical Structure Stock Photo Image By C Orangedeerstudio


Tooth Whitening Delhi Teeth Whitening In Delhi Dental Whitening Delhi



Pdf Stability Of Carbamide Peroxide In Gel Formulation As Prepared In Brazilian Compounding Pharmacies



Woa1 Antifungal Topical Composition For The Use In The Treatment Of Onychomycosis Google Patents



Preparation Optimization And Release Behaviour Evaluation Of Carbamide Peroxide Microcapsules Integrated With Eudragit Rs Xu Chemistryselect Wiley Online Library



Urea Hydrogen Peroxide 97 124 43 6 Sigma Aldrich



Amazon Com Teeth Whitening Gel Refill Usa Dentists Recommended Crystal Clear Teeth Whitening Fast Safe And Effective 35 Carbamide Peroxide Refills 5 Pack Beauty



Urea Hydrogen Peroxide Sigma Aldrich



7 Tooth Whitening



Preparation Optimization And Release Behaviour Evaluation Of Carbamide Peroxide Microcapsules Integrated With Eudragit Rs Xu Chemistryselect Wiley Online Library


